About Us
Chlamydia
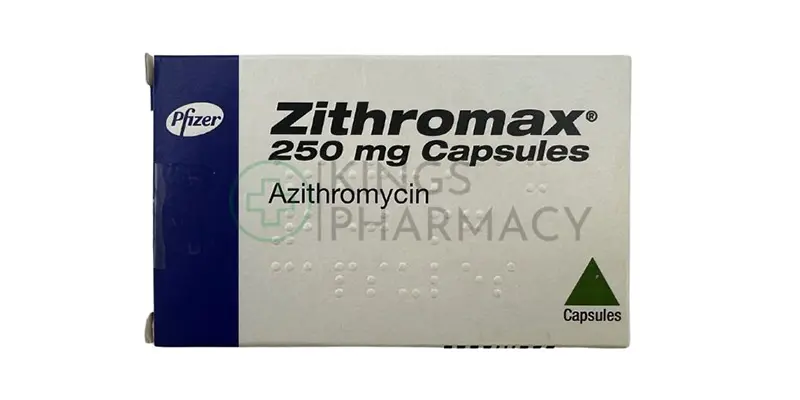
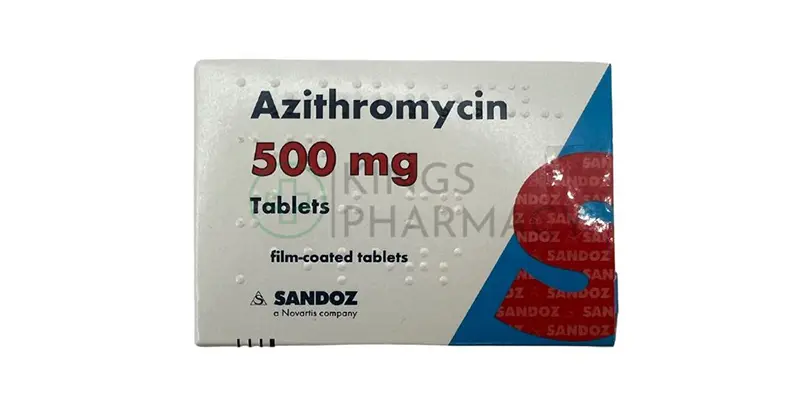
Chlamydia is a common sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium *Chlamydia trachomatis*. It often presents with mild or no symptoms, but if left untreated, it can lead to serious health issues like infertility and pelvic inflammatory disease. Treatment typically involves a course of antibiotics, such as azithromycin or doxycycline, which effectively eliminate the infection. It’s important for sexual partners to be tested and treated simultaneously to prevent reinfection. Regular screening and practicing safe sex can help prevent chlamydia and its complications.
Chlamydia is a common bacterial sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by Chlamydia trachomatis. It often affects the genital area but can also infect the rectum and throat. Chlamydia is especially common among young adults under 25.
Symptoms
Many people with chlamydia may not experience symptoms, which is why it often goes undiagnosed. However, if symptoms do occur, they can include:
In Women:
- Abnormal vaginal discharge
- Pain or burning when urinating
- Pain during sex
- Lower abdominal pain
- Bleeding between periods or after sex
In Men:
- Discharge from the penis
- Pain or burning when urinating
- Pain and swelling in the testicles (less common)
Chlamydia can also infect the rectum or throat, which may cause discomfort or discharge in the rectal area and a sore throat, though these symptoms are less common.
How it Spreads
Chlamydia is primarily spread through:
- Unprotected vaginal, anal, or oral sex with someone who has the infection
- Sharing sex toys without proper cleaning or condom use
Diagnosis
Chlamydia is diagnosed through a simple test, either a urine sample or a swab from the affected area (vagina, penis, rectum, or throat). Testing is available at GP surgeries, sexual health clinics, and sometimes through at-home testing kits.
Treatment
Chlamydia is easily treated with antibiotics, usually azithromycin or doxycycline. It’s important to:
- Complete the full course of antibiotics, even if symptoms go away
- Avoid sexual contact for seven days after starting treatment to prevent spreading the infection
- Get retested three months after treatment, especially if under 25 or at high risk
Self-Care and Management
- Inform sexual partners: Anyone you've had sexual contact with in the last six months should be notified so they can get tested and treated if necessary.
- Avoid sex until you and your partner(s) have completed treatment and any recommended waiting period.
- Follow up: A repeat test can confirm that the infection has cleared.
Preventing Transmission
- Use condoms during all types of sexual activity to reduce the risk of chlamydia and other STIs.
- Get regular STI screenings, especially if you are under 25 or have multiple partners.
- Avoid sharing sex toys or use a new condom on toys each time they’re shared or used with a partner.
Complications if Untreated
If left untreated, chlamydia can cause complications, especially in women, including:
- Pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which can lead to chronic pelvic pain, ectopic pregnancy, and infertility.
- Epididymitis in men, which can cause pain and swelling in the testicles.
- Reactive arthritis in both men and women, which can cause joint pain and swelling.
Chlamydia and Pregnancy
If you’re pregnant and have chlamydia, it’s important to get treatment. Untreated chlamydia can lead to complications such as premature birth and can be passed to the baby during delivery, potentially causing eye infections or pneumonia in newborns. Pregnant women with chlamydia may be offered a test of cure after treatment to ensure the infection is cleared.
Emotional Wellbeing
A chlamydia diagnosis can be upsetting, but remember that it’s treatable and very common. If you’re feeling anxious or distressed, consider:
- Talking with a counsellor or seeking support through STI support groups.
- Openly discussing with partners to ease concerns about transmission and support each other through treatment.
When to Seek Medical Advice
- If you have any symptoms of chlamydia or other STIs
- If you think you may have been exposed to chlamydia
- If your symptoms persist after treatment
- If you’re pregnant and suspect you may have chlamydia
Further Support
For more information or support, you can contact:
- Sexual Health Clinics – They offer confidential testing, treatment, and advice.
- NHS Services – NHS provides information on chlamydia and other STIs.
- Brook (for young people) – A UK-based service providing information and support on sexual health.
Chlamydia is common and treatable, and taking care of your sexual health is a step toward a healthier future. Regular testing and safe sexual practices can help prevent future infections.